
Red blood cells in plasma are an example of a suspension. Suspensions can be physically separated by centrifugation and do not possess the same interactions between solvent and solute that are found in a true solution. Suspensions are composed of large particles that float in a liquid.
Body fluid compartments measurement chemicals free#
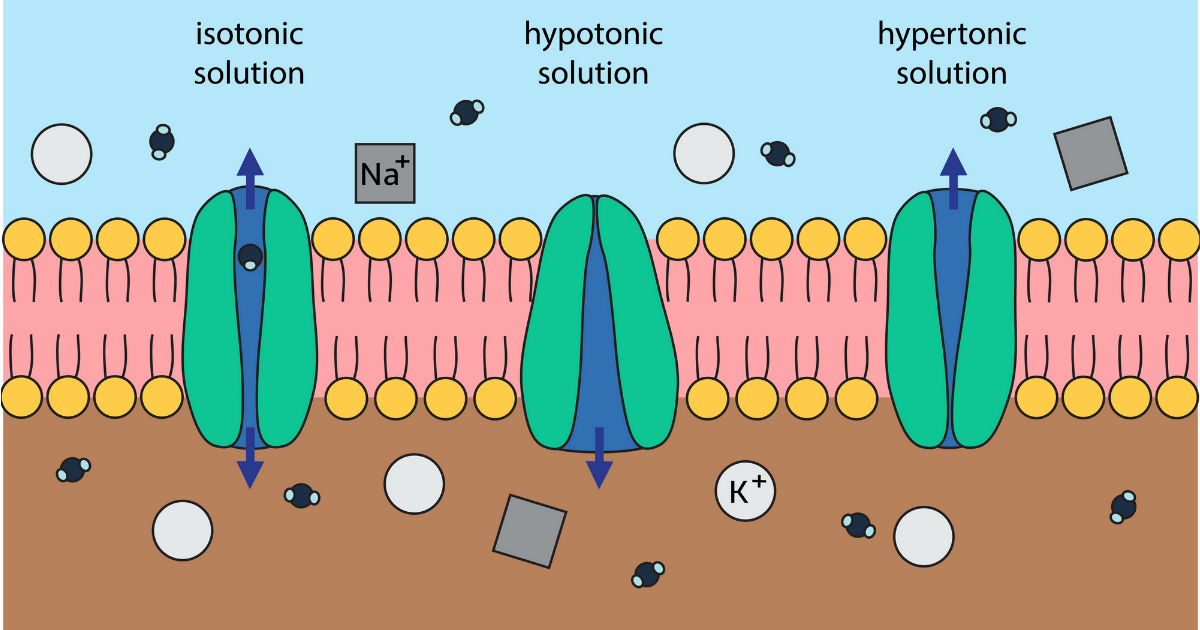
Physiologically, colloids provide very little free water to the patient’s system, and care should be taken not to create a hypotonic environment. The protoplasm inside cells is a common example of a colloid. These molecules are uniformly distributed throughout the dispersion, and they tend not to settle. Polar solvents, such as water, dissolve other polar covalent bonds nonpolar solvents dissolve nonpolar solutes: “Like dissolves like.”Ĭolloids (sometimes called dispersions or gels) consist of large molecules that attract and hold water ( hydrophilic: “water loving”).
The electrical properties of the solvent molecules determine how soluble a substance is for a particular solvent. When all three sets of forces are approximately equal, the two substances typically are soluble in each other. If the solute-solvent force is less than the solute-solute or solvent-solvent force, the solute does not dissolve. A solute dissolves in a solvent if the solute-solvent forces of attraction are great enough to overcome the solute-solute and solvent-solvent forces of attraction. These intermolecular forces must be broken before a new solute-solvent bond can be formed. The process of dissolving involves breaking the (relatively weak) bonds between the solute-solute molecules and the solvent-solvent molecules. Gases, liquids, and solids all can dissolve to become solutes. The medium in which it dissolves is called the solvent. The substance that dissolves is called the solute. One substance is evenly distributed between the molecules of the other. These substances and particles combine with water in the following three ways: as (1) colloids, (2) suspensions, or (3) solutions.Ī solution is a stable mixture of two or more substances in a single phase that cannot be separated using a centrifuge. Water is the primary component of any liquid within the body and has a great influence on the behavior of other materials as they are introduced. Water itself is a polar covalent molecule and is referred to in chemistry as a universal solvent. The body is based on liquid water chemistry and the interaction of various substances either dissolved or suspended within the fluid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
